SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) – a protocol for exchanging structured information in web services.
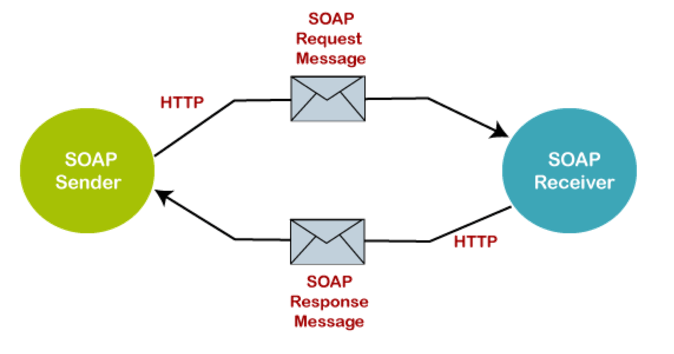
Key Features:
- Uses XML for message format,
- Follows strict standards, ensuring high security and reliability,
- Requires a WSDL (Web Services Description Language) file for service definitions.
Common Use Cases: Financial services, payment gateways, and applications requiring strong security and ACID compliance.
REST (Representational State Transfer) – an architectural style for designing networked applications, leveraging HTTP methods.
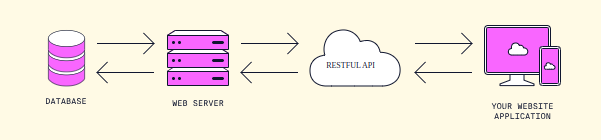
Key Features:
- Supports multiple data formats (e.g., JSON, XML),
- Lightweight and faster than SOAP,
- Stateless operations improve scalability.
Common Use Cases: Modern APIs, mobile apps, and public-facing web services.
XML (Extensible Markup Language) – a markup language for storing and transporting data.
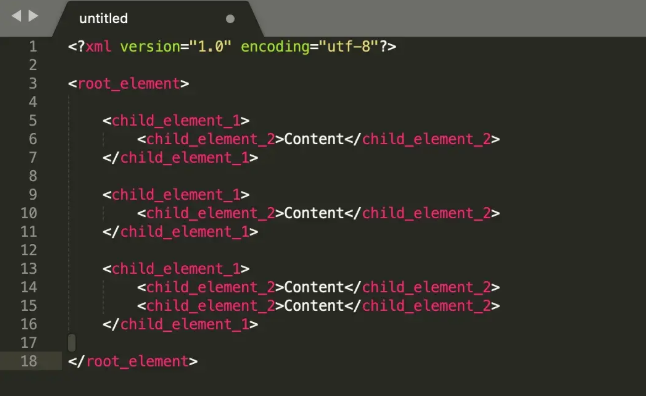
Key Features:
- Highly structured with user-defined tags,
- Used in both SOAP and legacy systems,
- Verbose, which can lead to larger payloads.
Common Use Cases: Document-based data exchanges, SOAP services, and configurations.
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) – a lightweight data-interchange format.
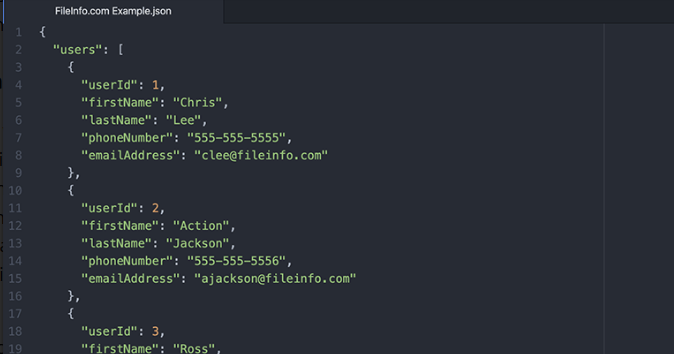
Key Features:
- Human-readable and easy to parse,
- Preferred for REST APIs due to compact size,
- Supports hierarchical data.
Common Use Cases: REST APIs, web and mobile apps, and configuration files.
SQL (Structured Query Language) – standardized language for managing and manipulating relational databases.
Key Features:
- Provides commands for:
- data retrieval (SELECT),
- insertion (INSERT),
- updates (UPDATE),
- deletions (DELETE),
- Supports data:
- definition (CREATE, ALTER, DROP) and,
- control (GRANT, REVOKE),
- Works with relational databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, and SQL Server.
Common Use Cases: Data analysis and reporting, backend operations for web and mobile applications, business intelligence, and data visualization tools.
MQ (Message Queues) – a technology for asynchronous communication between services or applications.
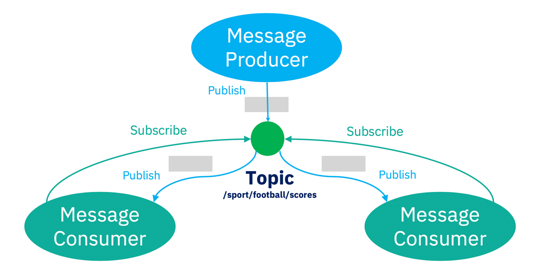
Key Features:
- Decouples producers and consumers,
- Ensures reliable delivery with durability and acknowledgment mechanisms,
- Examples include IBM MQ, RabbitMQ, and Apache Kafka.
Common Use Cases: Event-driven architectures, microservices, and handling high-throughput data streams.
Postman – a tool for testing and interacting with APIs.
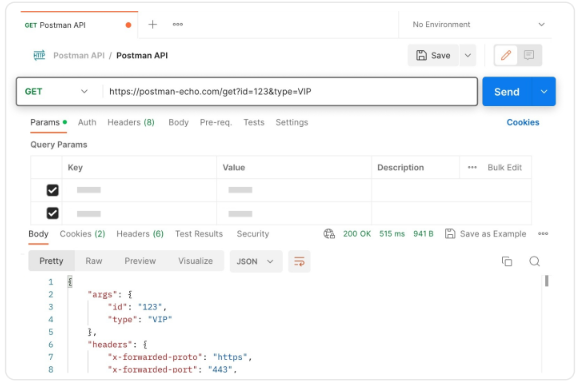
Key Features:
- Supports API development and testing for REST and SOAP services,
- Allows automation through collections and scripts,
- Integrates with CI/CD pipelines.
Common Use Cases: API testing, documentation, and mock server creation.
SoapUI – a dedicated tool for testing SOAP and REST web services.
Key Features:
- Comprehensive SOAP support with WSDL import,
- Advanced testing features like security and load tests,
- It is less intuitive than Postman for REST APIs.
Common Use Cases: Testing SOAP services and enterprise-grade REST APIs.
Sources:
